2.2.5: Environmental Variables
Learning Objectives
Understand the purpose of the
.envfile and dotenv packageImplement the dotenv package in a React Application and store environmental variables
Use environmental variables stored in the
.envfile in ReactUse enviromental variables in the backend - Module 3 onwards
Introduction
When consuming third party API’s, developing databases and deploying servers you may want to obscure vital and secretive data that is used in your application. Use the NPM package dotenv combined with the .gitignore file so that you never push sensitive data online always keep your information safe. Use a .env file to hide information such as database credentials, API keys, secrets and even your port number. It is imperative you use a dotenv as your API keys may be paired to a credit card and we want to make sure you are not exposing yourself or your future company to potential risks.
Dotenv is a zero-dependency module that loads environment variables from a
.envfile intoprocess.env. Storing configuration in the environment separate from code is based on The Twelve-Factor App methodology.
dotenv in React
Usually we would need to install dotenv into our applications, but as we are developing in a React environment we can just create a .env file and start putting our credentials in there. This is because react-scripts is able to process .env files whenever you run the command npm run dev, which means you will be able to use these hidden credentials in your application, but if you edit it you must completely restart the React App.
If you would like to checkout the documentation further look at this set of documentation.
Note there are different implementations of dotenv in different environments, in this set of documentation pay attention to the React example.
You will need to create a
.envfile in the root level of your React project.Store your sensitive data inside the
.envfile.Note when developing .env files within a React application you must prefix its name with: VITE
_SOME_...You will need to reference it with the same prefix:
import.meta.env.VITE_SOME_...
Ignore your .env file within the
.gitignorefile.Create a .env.sample file to indicate what credentials are required in your application.
Remember if you alter your .env file you may need to restart React application, stop your server and run
npm run dev.
Sample Folder Structure


Use cases for the .env?
When developing your applications you might be wondering what information you should share with collaborators and what you should never share. If you are developing an application that consumes or is connected to a third party that requires payments, you will be given keys or secrets to validate your account, this information should be placed in the .env and hidden from everyone but yourself.
If a key or secret that is linked to a credit card is accidentally put onto GitHub, this could have dire consequences. When developing with the paid subscriptions of APIS such as Spoonacular API or even Google Cloud API you will want to hide your API key as if its accidentally put onto GitHub, you could be charged hundreds or even thousands as people steal and use your key to power your own application. You will then need to generate new keys, remove your application from GitHub and perhaps even stop your credit card.
API keys are not the only thing that should be stored in the .env file, database credentials as well as environmental details such as the port number should be safely hidden away. If a malicious developer was afforded the chance they would be able to steal all of the information stored and even delete the data. So save yourself and your potential companies time by securely storing your sensitive data in a .env file.
dotenv and the Backend
When you create your backend using ExpressJs and NPM, you will quickly realise that we don't have the internal React tools that would automatically create the .gitignore and process .env file within your application. To use dotenv within an NPM or backend project we will need to follow the documentation online. When you use enviromental variables within an Express application you will need to install the package into the npm directory.
Run the command
After the installation has been completed you can create your .env file within the root of the backend directory.
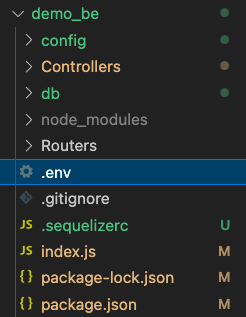
You can create the enviromental variables in the same way that we have developed them for our React applications.
When using the .env to refernce your credentials within your file, you will need to add the highlighted line above any reference. That way your code is able to extract the information required within the .env.
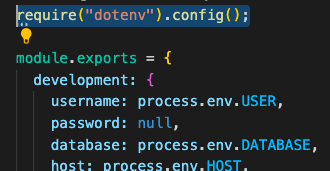
It should be noted that like React if you update the dotenv you will need to restart the application.
Last updated