0.3: GitHub
Learning Objectives
Introduction
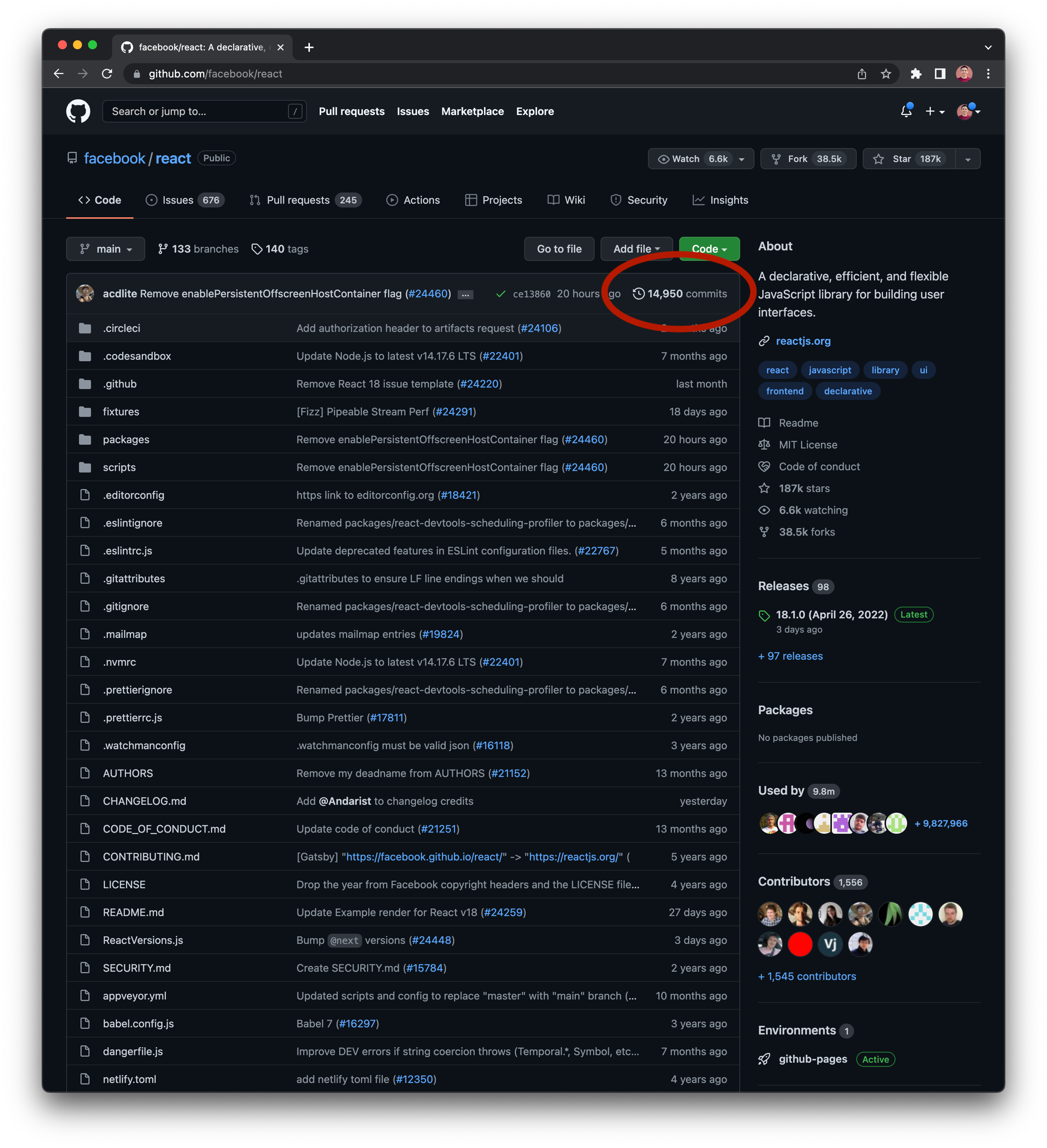
GitHub Workflow Summary
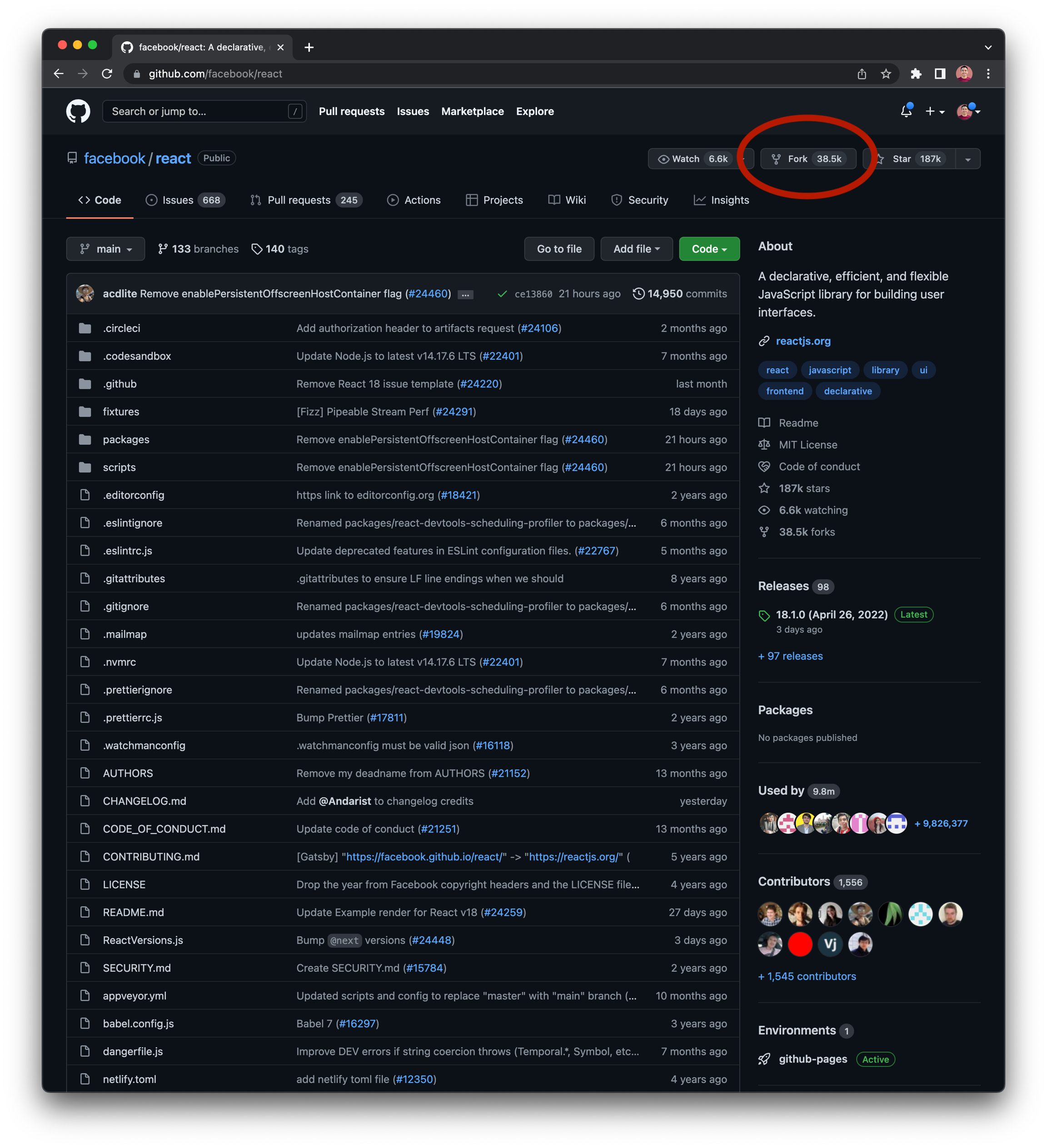
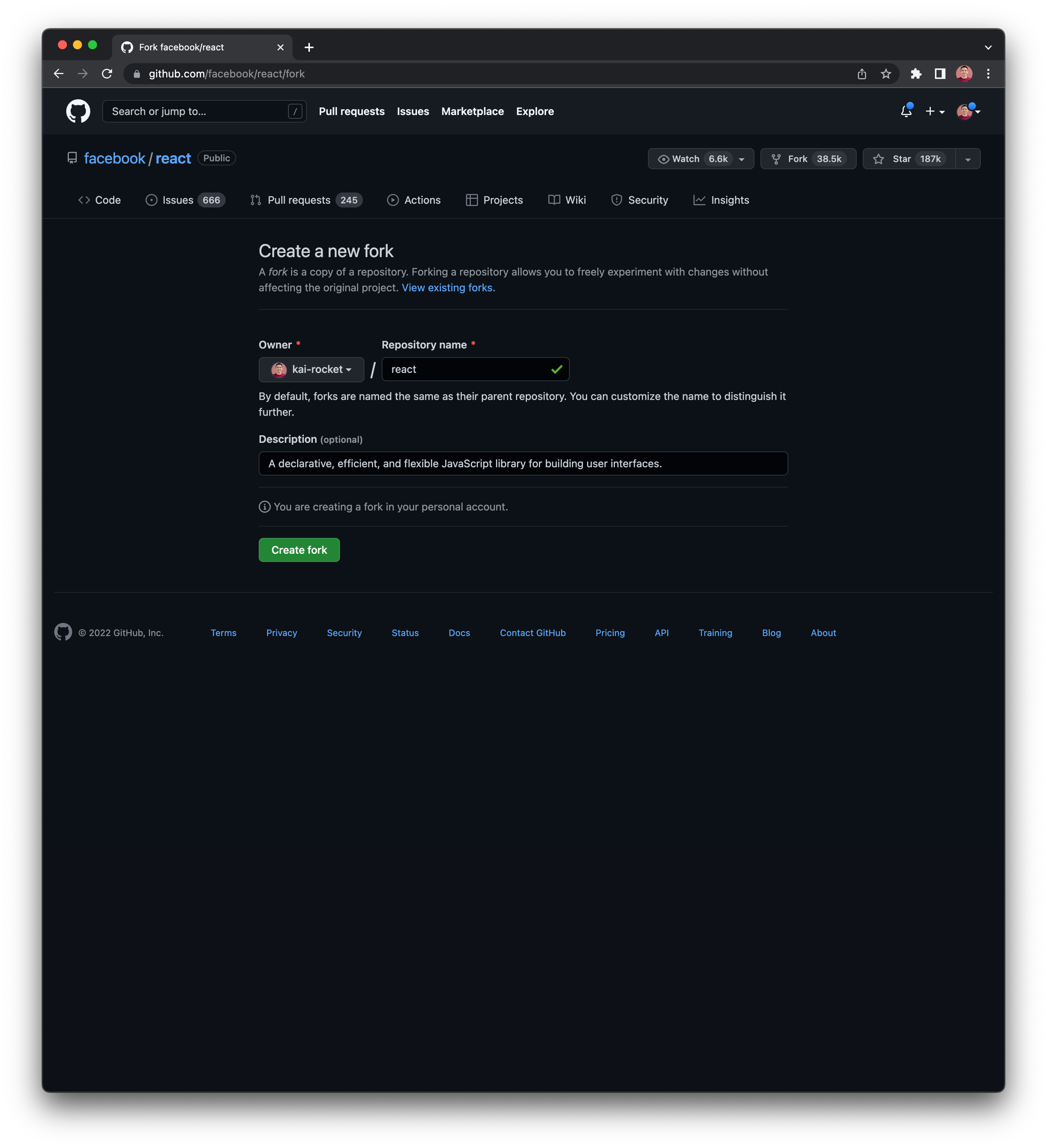
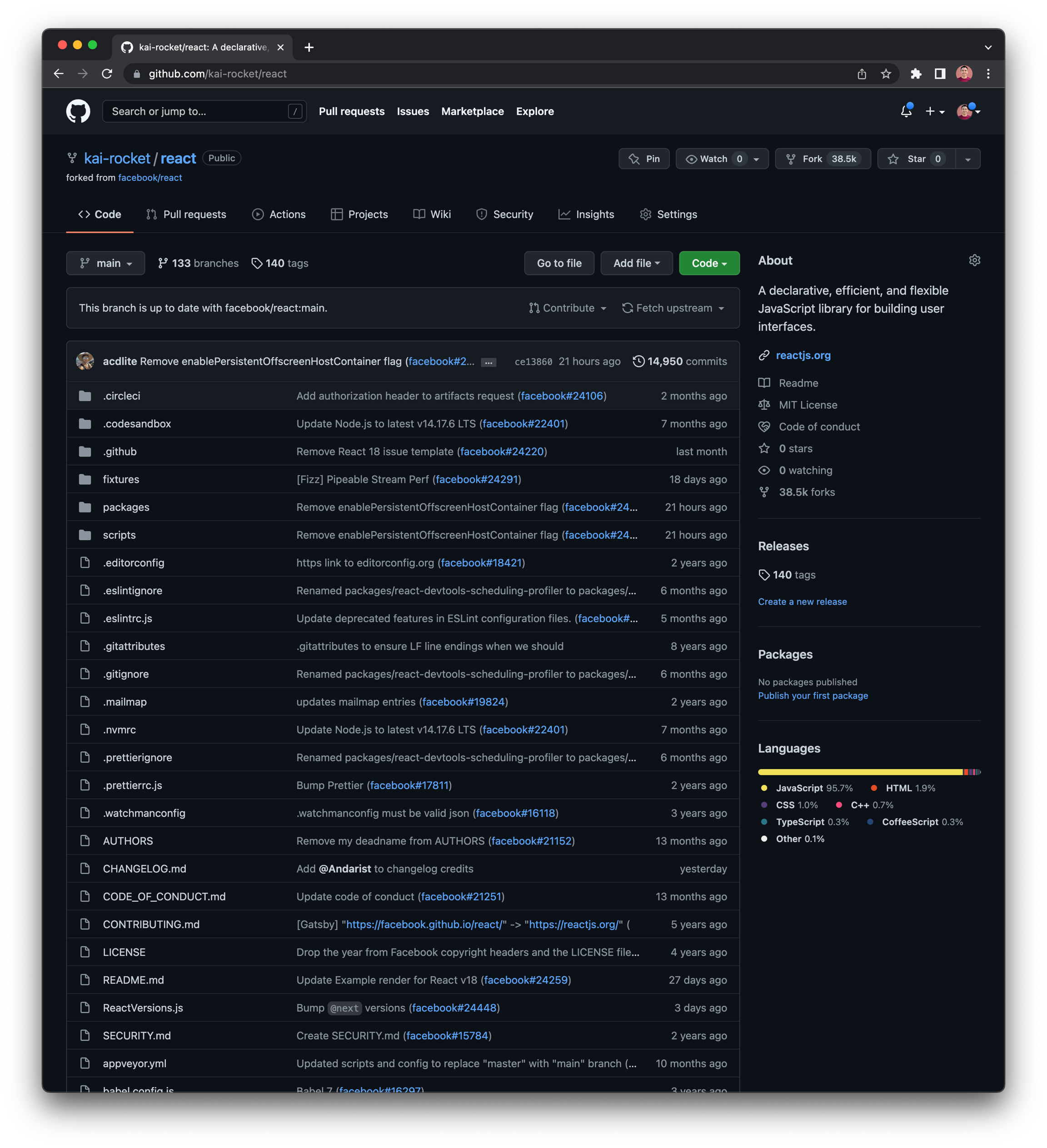
GitHub Fork
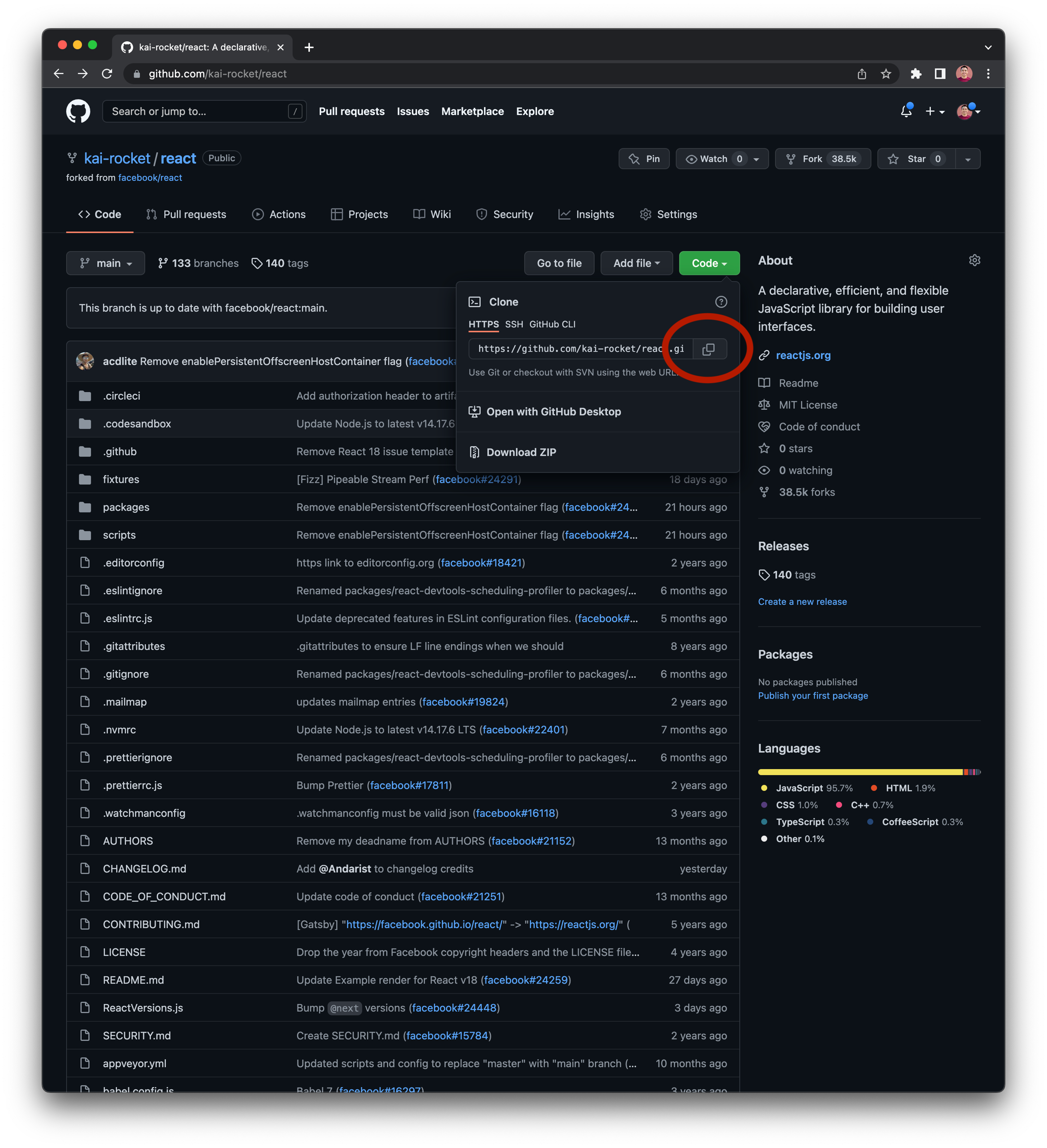
Git Clone
Git Push
Git Pull
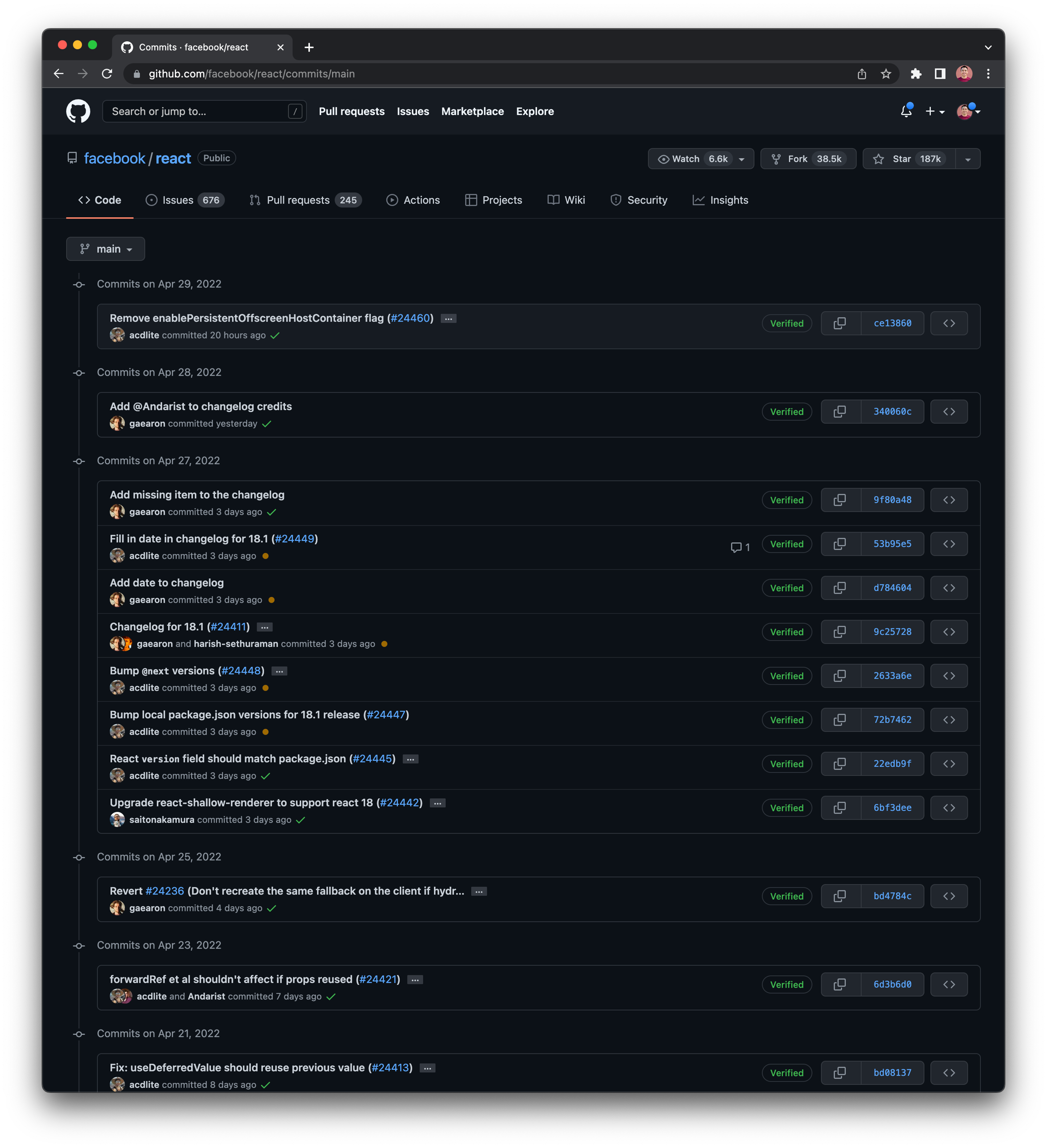
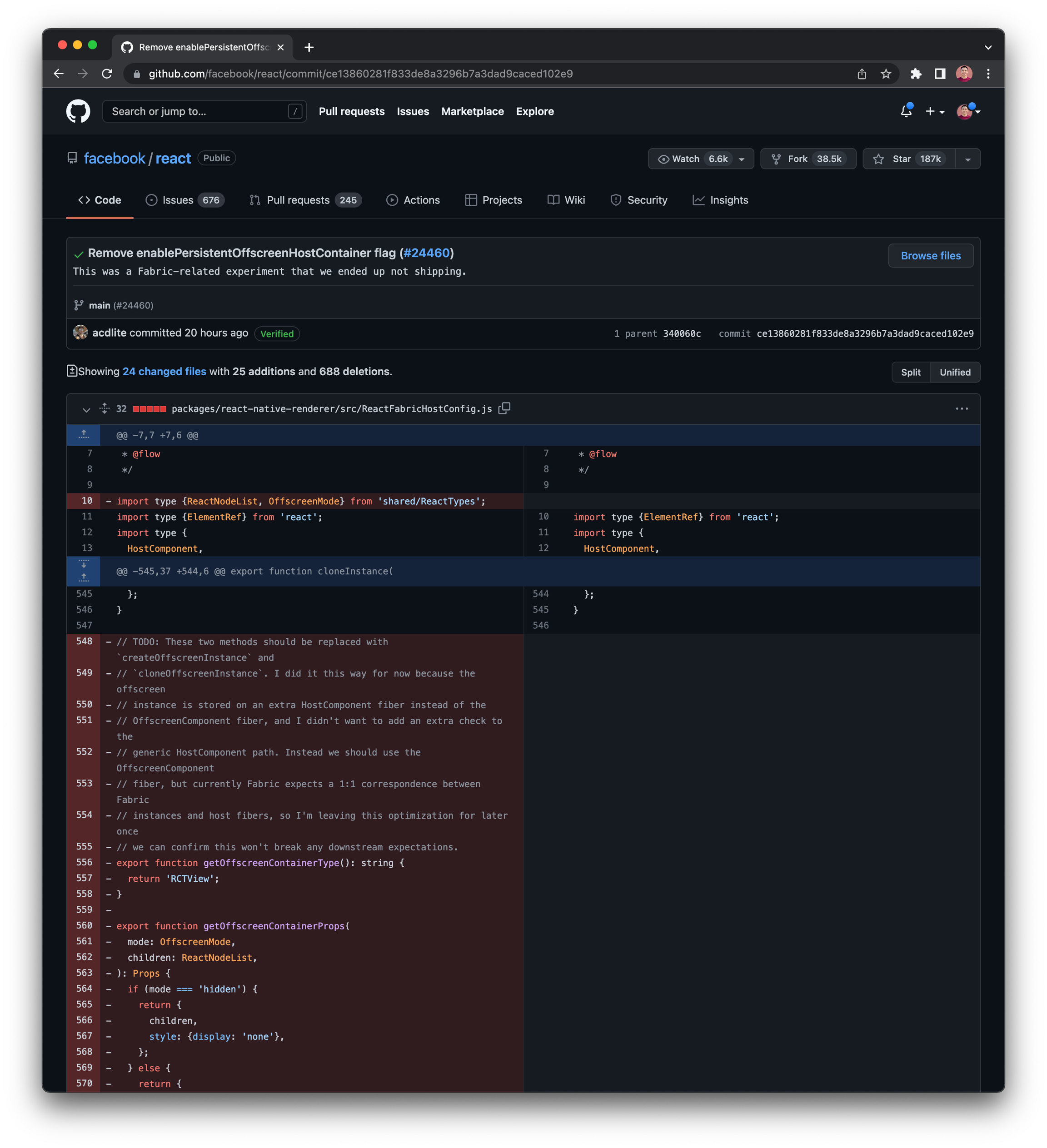
How to view commit history in GitHub